Maria Cramer, Graduate Student | mec@umd.edu and Kelly Hamby, Extension Entomologist | kahamby@umd.edu
University of Maryland, Department of Entomology
As soybean plants mature, tolerance for defoliating pests drops from about 30-35% during the vegetative stages to closer to 15-20% during the reproductive stages (flowering and pod fill). Any defoliation can look worrying, but it is hard to accurately measure defoliation. Most people tend to overestimate damage in three ways: overestimating the leaf area lost, not taking the full plant canopy into consideration, and not sampling the field randomly. Luckily, there are some great new tools to help you measure accurately and train your eye. Accurate measurement is the key to avoiding unnecessary treatments, saving you money, time, and preserving beneficials.
What defoliates soybean?
- Grasshoppers tend to be concentrated on the edge of the field, especially near grasses or small grain fields1, and can cause jagged holes in leaves and sometimes clip pods (Fig. 1a).
- Japanese beetle is an introduced pest that aggregates in large groups and skeletonizes leaves (Fig. 1b).
- Bean leaf beetle is a native pest that can cause damage to seedlings, defoliate, and occasionally feeds on pods, but generally is not a problem on large plants unless other defoliators are abundant (Fig. 1c).
- Mexican bean beetle occurs late in the season and feeds on the underside of leaves, causing a lacy appearance (Fig. 1d ).
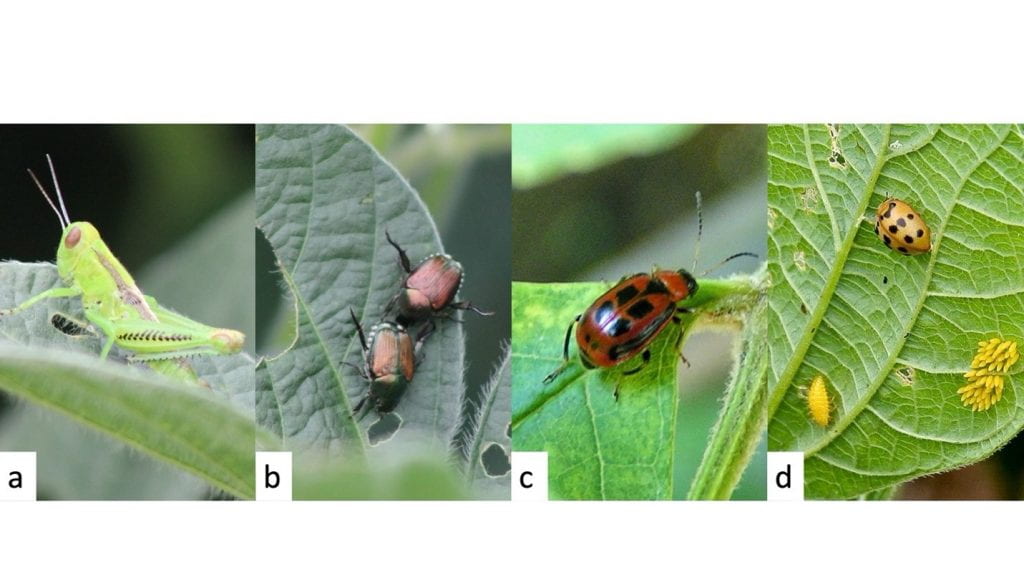

Figure 1. a) Grasshopper, photo from Prairielands FS. b) Japanese beetle, photo from Prairielands FS. c) Bean leaf beetle (they can also be yellow or lack spots), photo by Wikimedia Commons. d) Mexican bean beetle, photo from University of Maryland Extension.
There are also caterpillars that can feed on soybean foliage.
- Soybean looper is distinctly larger towards its tail-end, has two pairs of prolegs in the middle of its body, and moves in a “looping” fashion (curls its body into a hump while walking) (Fig. 2a).
- Silver spotted skipper has thin stripes and a dark head-capsule, with a noticeable constriction (narrower) behind the head (Fig. 2b).
- Green cloverworm looks similar to soybean looper and also moves in loops (notice hump forming in the image), but the two ends are the same size, and it has three pairs of prolegs in the middle of its body (gripping the stem in the image) (Fig. 2c).
- Velvetbean caterpillar has four pairs of prolegs in the middle of their body and can also be identified by its violent thrashing when handled (Fig. 2d).
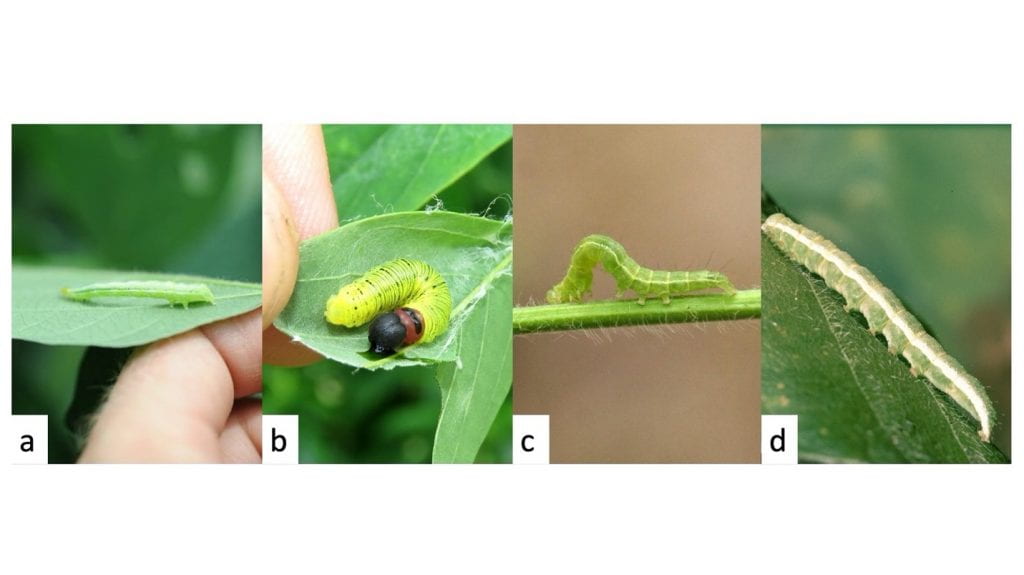
Figure 2. a) Soybean looper, photo by NCSU extension. b) Silver-spotted skipper, photo by Josh Em. c) Green cloverworm, photo by Daren Mueller. d) Velvetbean caterpillar, photo by Clemson University.
These pests make up the defoliating insect complex in soybeans, although they do not necessarily all occur together. However, if you must treat for them, make sure your insecticide works against the complex that is in your field.
When is defoliation a problem?
These insects become a problem when their defoliation exceeds treatment thresholds. Vegetative soybeans are tolerant of feeding, especially as they get larger, so until up to about two weeks prior to blooming this is around 30-35%. From about two weeks prior to blooming until pods fill (R7-R8) the treatment threshold is 15-20% defoliation. If defoliation exceeds these numbers at these times, yields can start declining, especially in drought conditions2. Pests that feed on pods (including some caterpillar species), have different thresholds, so it can be important to identify specific pests during sampling.
Sampling
To accurately determine percent defoliation, a thorough assessment of the field is necessary. Because many defoliators tend to congregate in the field, this means sampling a minimum of ten plants in four locations and averaging the results is needed for an accurate assessment. Figure 3, from the University of Nebraska Extension, outlines how to properly sample. Although this is a lot of sampling, it is important to eliminate bias and avoid overestimating damage. Nebraska Extension also has a work sheet3 to plug in your measurements for an average.

If you see caterpillar pests in your field, you may also want to use sweep net sampling4 to determine which pests and how much pressure is present. The threshold for velvetbean caterpillar is ≥10 in 10 sweeps, and for soybean looper it is ≥15 in 10 sweeps. Corn earworms (Fig. 4.) which feed on terminals, flower clusters, and pods and can also be sampled using sweep nets. A dynamic threshold calculator5 has been developed for corn earworm in soybeans.

New technology
Some good news is that even though it is hard to visually gauge defoliation, there are new tools you can use to be more accurate. One is the Crop Protection Network’s Soybean Defoliation Training6. With this tool you can use a slider to see what different levels of defoliation look like on a leaf. You can also test your skills by taking a quiz where you estimate defoliation. This is a great way to train your eye before you go out to sample.
Alternatively, if you have a smartphone, you can use a new app called “Leafbyte” to accurately assess defoliation7,8. With this app, you take pictures of leaves on a white background and the app calculates the percentage of leaf removed (Fig. 5).
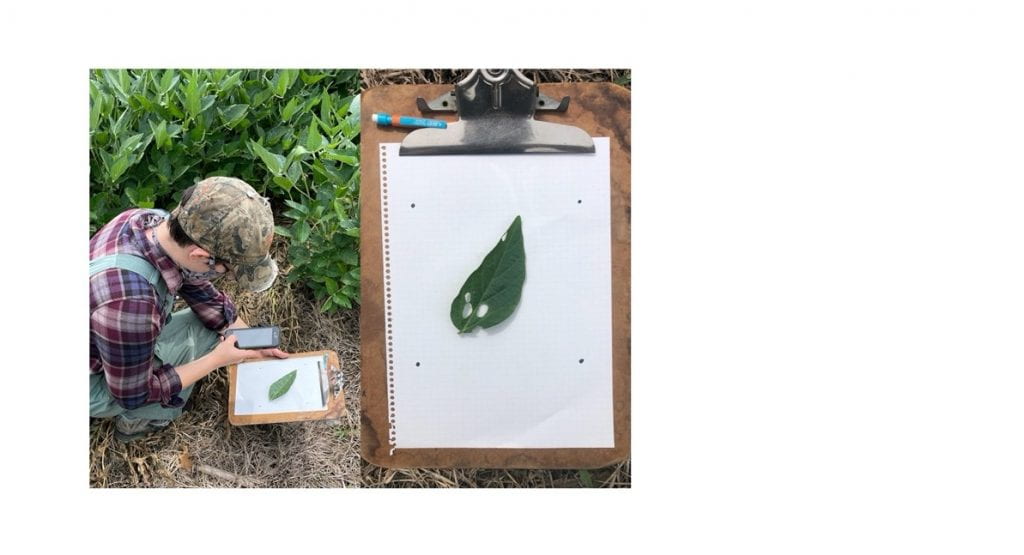

Treatments
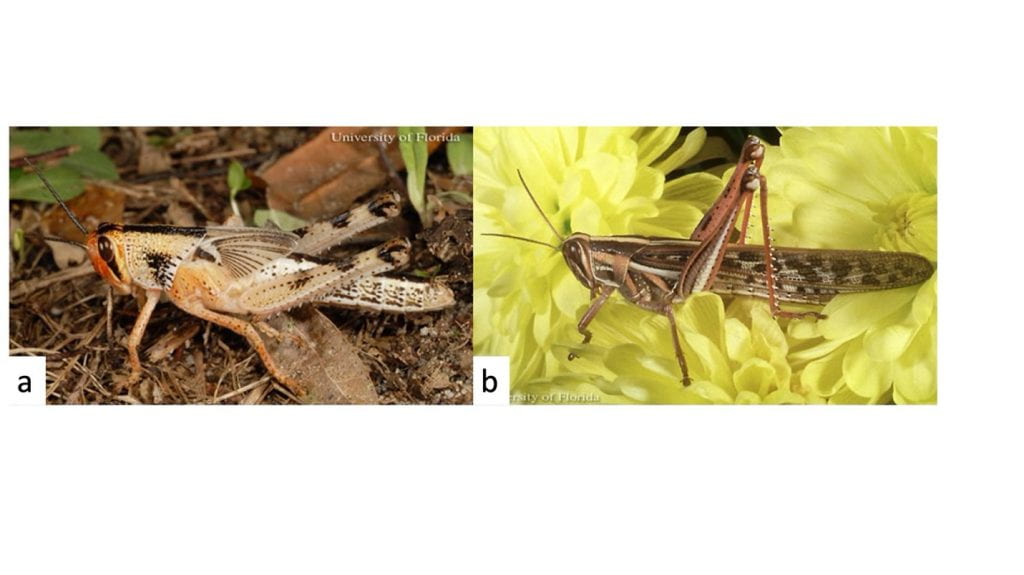
For many of these pests, avoiding broad-spectrum insecticides early in the season is likely to keep their populations in check. However, if defoliation has exceeded treatment threshold, you have several options; remember that less mature insects are easier to control. For most of these pests, pyrethroid products (e.g., Baythroid®, Warrior II®, Hero®) are reasonably effective and provide residual control. Soybean looper is an exception, because it has evolved resistance to pyrethroids, carbamates, and organophosphates (and other modes of action in the lower coastal plain areas of North Carolina), so it will not be controlled if these insecticides are used for other pests. Indoxacarb (e.g., Steward®), methoxyfenozide (e.g., Intrepid®), chlorantraniliprole (e.g., Coragen®, Prevathon®), spinosyns (e.g., Radiant®, Blackhawk®), and methoxyfenozide/spinetoram mixtures (e.g., Intrepid Edge®) can be effective9,10. Large grasshoppers require a higher rate of pyrethroid insecticides, while grasshopper nymphs (those without fully formed wings, Fig. 6) can be controlled using the insect growth regulator diflubenzuron (Dimilin®)11. When using insecticides, always consult and follow the label.
Additional resources:
- Boethel DJ. Integrated management of soybean insects. Soybeans Improv Prod Uses. 2004;(16):853-881. doi:10.2134/agronmonogr16.3ed.c17
- Klubertanz TH, Pedigo LP, Carlson RE. Reliability of yield models of defoliated soybean based on leaf area index versus leaf area removed. J Econ Entomol. 1996;89(3):751-756. doi:10.1093/jee/89.3.751
- Soybean defoliation worksheet: https://cropwatch.unl.edu/2016/soybean-defoliation-worksheet
- Sweep-net sampling: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QiokQqLFD5U&t=1s
- Podworm dynamic calculator: https://www.ces.ncsu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/CEW-calculator-v0.006.html
- Defoliation estimation training: https://severity.cropprotectionnetwork.org/crop/soybeans/soybean-insect-defoliation-training
- Getman-Pickering ZL, Campbell A, Aflitto N, Grele A, Davis JK, Ugine TA. LeafByte: A mobile application that measures leaf area and herbivory quickly and accurately. Methods Ecol Evol. 2020;11(2):215-221. doi:10.1111/2041-210X.13340
- Leafbyte app: https://zoegp.science/leafbyte
- Cook DR, Crow W, Gore J, Threet M. Performance of selected insecticides against soybean looper in soybean, 2020. Arthropod Manag Tests. 2021;46(1):2021. doi:10.1093/amt/tsab020
- Reisig D. Soybean looper thresholds and insecticide recommendation. NC State Extension.
- Royer TA, Giles KL, Jeffcoat MD, Griffin J. Evaluation of Dimilin insecticide for control of a mixed-species grasshoppers using an RAAT application, 2000. Arthropod Manag Tests. 2001;26(1):10-11. doi:10.1093/amt/26.1.g54
