Alyssa Koehler, Extension Field Crop Pathologist | akoehler@udel.edu
University of Delaware
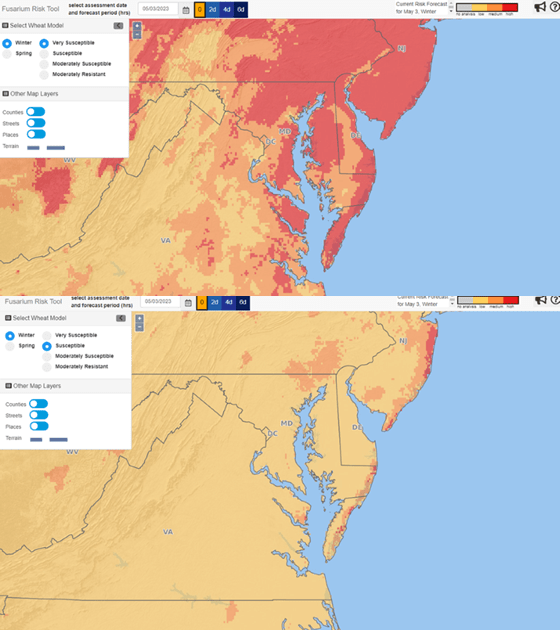
Wheat anthesis (flowering) is underway and will be continuing for the next 1-2 weeks across the region. Up until the rains this past weekend, we have been at low FHB risk. We are currently tracking as medium-high risk for very susceptible varieties and low-medium risk for varieties with some level of resistance (Figure 1). If you are planning for wheat fungicide application, scout frequently, looking for yellow anthers in the center of the wheat head (Figure 2) to signal that flowering has begun (Feekes 10.5.1). Depending on the weather, we can usually expect flowers to start showing up on wheat heads 3-5 days after full head emergence, with cool weather this can stretch this process out to 7-10 days. Anthers can remain attached after flowering, but become a pale white. For best mycotoxin (DON) control, it is better to be at flowering or a few days beyond than to spray too early when heads are not out yet (especially those secondary tillers). Fungicide products should be applied at the manufacturers recommended rate with nozzles angled 30-45° from horizontal (30 degrees is better than 45). Nozzles angled both forward and backward or twinjet nozzles that spray in two directions give better contact with the head and increase fungicide efficacy. For ground sprays, fungicides should be applied in at least 10-15 gallons of water per acre; aerial applications are recommended at 5 gallons per acre.

Once wheat has flowered, symptoms of FHB are usually visible in 18-24 days, but cool weather can slow symptom development. Heads with FHB will have bleached florets or bleached sections of the head and may have pink growth on spikelets. Glume blotch may also be present, but typically has more of a grey appearance. You can follow these steps to assess the severity of FHB present in your field.
- For every 10 acres of field, randomly select one spot to survey.
- Keeping your line of sight above the wheat heads, walk 40-50 yards and randomly pick 10-20 heads to look at on the plant or detach and place into a bag. (Looking down may bias the heads you select).
- Once you have randomly collected the heads, rate the percent of each head with symptoms of FHB (bleaching or pink growth on spikelets). You can use the scale below to help calibrate your eye (next page).
- After you have recorded values for each head, determine the average percent FHB severity by dividing the sum of disease severities by the total number of heads collected. (Ex. You rate 10 heads with severity values: 0%, 10%, 30%, 0%, 0%, 20%, 10%, 0%, 0%, 0%. These add up to 70. 70/10 heads = 7% overall FHB severity). Higher levels of FHB are typically associated with elevated levels of DON and possible issues with yield and test weight. It is possible to have delayed or lower levels of symptoms and still have DON.
- Repeat this assessment as needed to get an overall rating for the field. Fields with greater than 10% FHB severity are at higher risk for yield losses or elevated DON. Fields with elevated DON should be harvested as early as possible and you may want to consider increasing combine fan speeds and shutter openings to reduce the amount of scabby kernels harvested.
